Is Diabetic Retinopathy Reversible?
Sadly, diabetic retinopathy can’t be reversed.
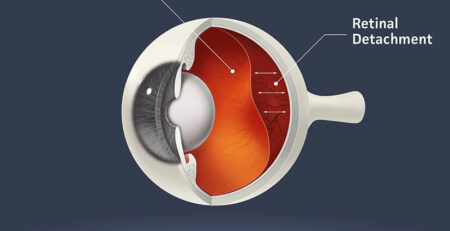
Diabetic retinopathy, a leading cause of vision loss, occurs due to the long-term consequences of diabetes. As blood sugar levels remain elevated over extended periods, the delicate microvascular network within the retina, the light-sensitive layer at the back of the eye, begins to suffer irreversible damage. If left untreated, this damage can lead to a gradual loss of eyesight and perhaps total blindness.
Understanding the Pathophysiology of Diabetic Retinopathy
The journey of diabetic retinopathy begins with the slow degeneration of the capillaries, the smallest blood vessels in the retina. These capillaries, responsible for supplying oxygen and nutrients to retinal tissues, are damaged by persistent high sugar.
As high sugar levels persist, the walls of these vessels thin out, leading to the formation of microaneurysms – small blood vessels. These blood vessels are weak and leak out, which becomes the initial hallmark of diabetic retinopathy.
Microaneurysms become a permanent presence in the retina once they appear. Despite future attempts to treat diabetes, these microaneurysms do not go away; instead, they serve as a permanent reminder of the years of blood vessel damage.
However, early detection of diabetic retinopathy can significantly slow down its progression from stage 1 to stage 2 or 3.
How to Reduce the Progression of Diabetic Retinopathy?
Vision loss due to diabetic retinopathy can’t be reversed. However, early detection and regulating blood sugar levels at an early stage can help to prevent further vision loss. Here are a few steps that you can take to stop diabetic retinopathy from getting worse:
Diabetic Management: Careful diabetes management can sometimes treat mild cases of diabetic retinopathy. To manage your diabetes:
- Regularly monitor your blood sugar level
- Follow a balanced diet
- Engage in regular physical activity
- Change lifestyle habits like quitting smoking
Regular Eye Exam: If you have diabetes, you should get a dilated eye exam at least once a year, even if you don’t have any symptoms of vision problems. This is because early detection and treatment of diabetic retinopathy can help prevent vision loss.
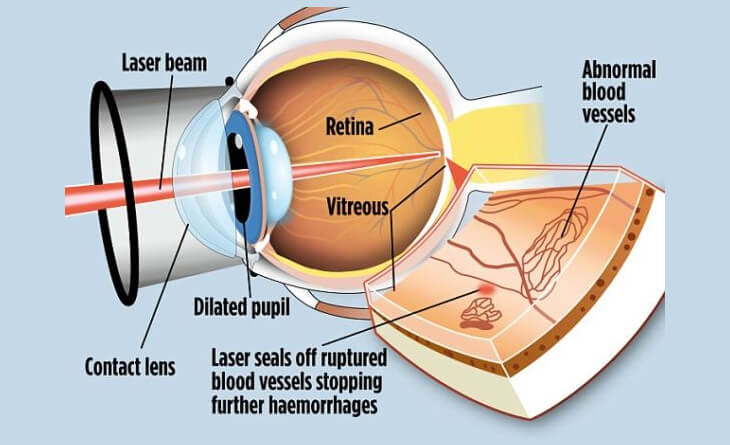
Laser Photocoagulation: For advanced stages of diabetic retinopathy, your eye specialist in Delhi may recommend laser photocoagulation to seal leaky blood vessels and prevent further damage. This procedure is minimally invasive and can effectively preserve vision.
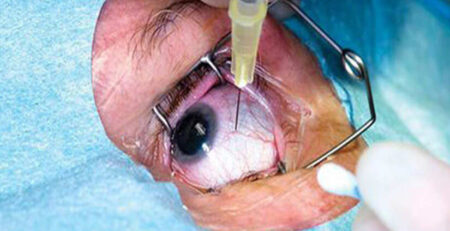
Intravitreal Injections: Intravitreal injections are used to deliver medication to the retina directly. Intravitreal injections for diabetic retinopathy are often divided into two types: anti-VEGF injections and steroidal injections. Anti-VEGF drugs work by blocking the action of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF). Whereas steroid injections can help decrease retinal inflammation, which can lead to diabetic retinopathy.
Diabetic retinopathy injections can be costly. The diabetic retinopathy injection cost depends on several factors, including the type of medication used and number of injections required.
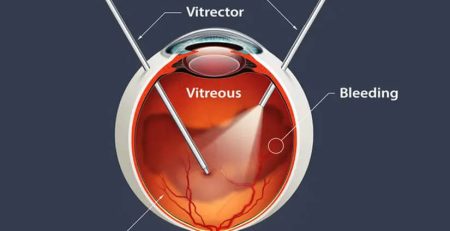
Vitrectomy: In severe cases of diabetic retinopathy, a vitrectomy may be necessary to remove scar tissue or blood from the vitreous cavity, the clear gel-like substance in the back of the eye. This procedure is typically performed as a last resort to restore vision.
Diabetic retinopathy is challenging, but with careful blood sugar management, regular eye exams, and timely treatment, you can significantly reduce the risk of vision loss. If you are dealing with diabetic retinopathy, consult with Dr Anisha Gupta.