Everything You Need to Know About Retinal Detachment
Have you ever experienced a sudden change in your vision, like seeing flashes of light or a dark curtain floating over your field of vision?
These could be signs of a retinal detachment, a serious eye condition that occurs when the retina, the light-sensitive tissue at the back of your eye, pulls away from its underlying layer. If left untreated, retinal detachment can lead to permanent vision loss or even blindness.
But fear not! In this comprehensive guide, we will explore retinal detachment’s causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment options, including retinal detachment surgery and preventive measures. Keep reading!
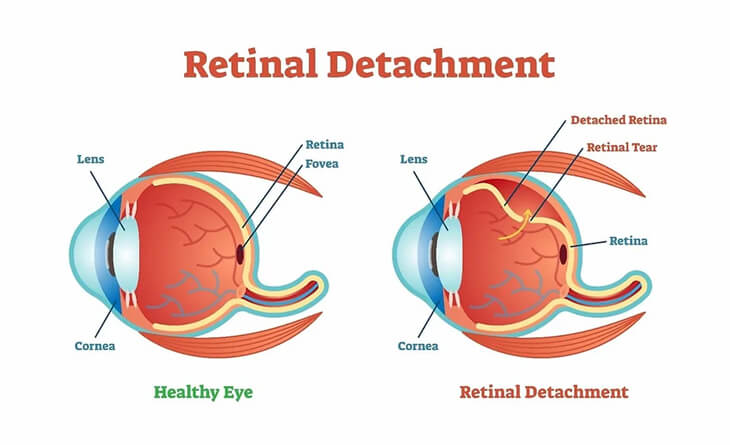
What is Retina?
Before diving deep into retinal detachment, we will first understand the term retina.
The retina is a thin, light-sensitive tissue layer lining the back of the eye. As light enters your eye, the lens focuses it onto the retina. The retina transforms this image into electrical signals that travel through the optic nerve to your brain. The retina, cornea, lens, and other components of your eye and brain work together to create normal vision. The retina contains two main types of photoreceptor cells: rods and cones. Rods are responsible for vision in low light, while cones are responsible for colour vision and vision in bright light.
Sometimes, due to various reasons, the retina gets pulled away from its normal position, which could lead to vision loss.
What is Retinal Detachment?
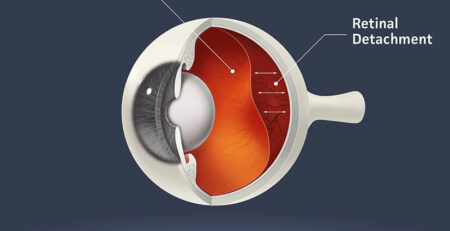
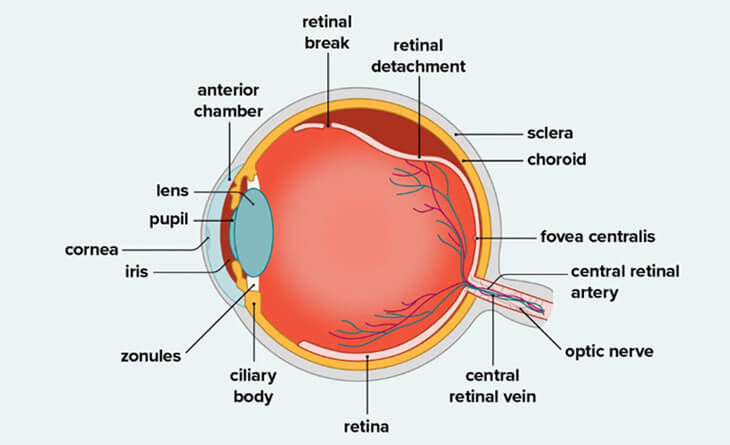
A retinal detachment is a severe eye condition that occurs when the retina is pulled away from its usual position due to various factors, such as a tear or hole in the retina, inflammation or swelling, or medical conditions like diabetes and hypertension.
When the retina is detached, fluid accumulates behind it, preventing it from receiving the nutrients and oxygen it needs to function properly. This can lead to vision loss, which can be permanent if not treated promptly.
There are three types of retinal detachment:
- Rhegmatogenous: Rhegmatogenous retinal detachment is the most common type, and it occurs when there is a hole or tear in the retina. This allows fluid to accumulate between the retina and the wall of the eye, causing the retina to detach. It can occur due to various reasons, including vitreous detachment, trauma, myopia, age-related changes, genetics and previous eye surgery.
- Tractional: Tractional retinal detachment occurs when scar tissue pulls the retina away from the wall of the eye. This can happen after an eye injury, or it can be caused by conditions such as diabetic retinopathy, vascular occlusion, vasculitis and uveitis.
- Exudative: Exudative retinal detachment occurs when fluid accumulates behind the retina despite the absence of a retinal tear. As the fluid accumulates, it pulls the retina away from the supporting tissue. The primary causes of this fluid accumulation are leaky blood vessels or swelling behind the eye, often associated with conditions like uveitis, an inflammatory eye disorder, central serous chorioretinopathy or certain eye tumors.
What Are the Symptoms of Retinal Detachment?
Retinal detachment is not painful. However, warning signs nearly always arise before the event begins or has progressed. The most common symptoms of retinal detachment are as follows:
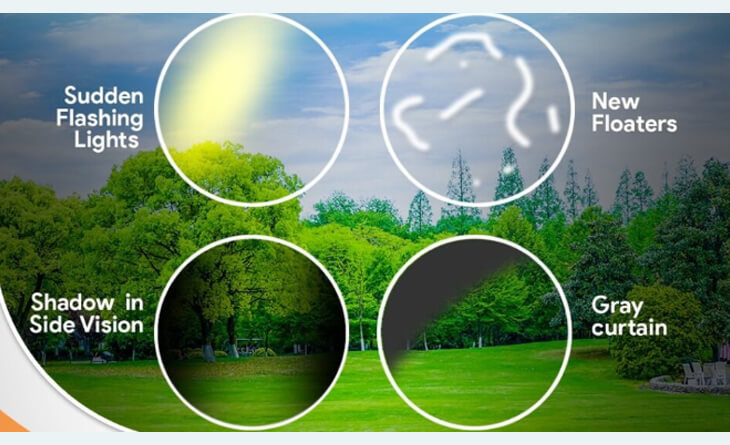
Sudden Increase in Floaters: Floaters are small, dark spots or cobweb-like shapes that move across your field of vision. They are usually harmless, but a sudden increase in floaters can signify retinal detachment.
Flashes of Light (Photopsia): These sudden flashes of light, usually in the peripheral vision, can come and go.
Blurred or Decreased Vision: This may start in one part of your vision and can gradually worsen.
A Curtain-Like Shadow Over Your Field of Vision: This may start as a small shadow in your peripheral vision, but it can quickly grow and cover your entire field of vision.
If you experience any of these symptoms, you should seek an eye specialist in Delhi immediately because early diagnosis and retinal detachment treatment can help prevent vision loss.
Diagnosis and Prevention of Retinal Detachment
A proper diagnosis is essential to create a treatment plan for retinal detachment. Therefore, your eye specialist will perform a comprehensive eye exam to diagnose it. During this exam, your doctor will dilate your pupils using eye drops to enlarge them and provide a better view of the retina. They will then use a special instrument called an ophthalmoscope to examine the retina for detachment, and subsequently its cause like retinal tears/holes, diabetic retinopathy and vascular occlusion.
In some cases, if the doctor suspects retinal detachment, they may order additional tests, such as:
Optical Coherence Tomography (OCT): OCT is a non-invasive imaging test that uses laser light to create detailed cross-sectional images of the retina. This can help your eye specialist in Delhi see the layers of the retina and identify any abnormalities. This is especially useful in tractional and exudative retinal detachments, to look for status of macula ( central part of retina) and to look for any causative lesions.
Fluorescein Angiography: This test involves injecting a fluorescent dye into a vein in your arm. The dye travels through your bloodstream and reaches the retina. The ophthalmologist will then take pictures of the retina as the dye circulates. This test can help to identify any areas of leakage or damage to the retina.
Ultrasound: In this test, your eye specialist in Delhi uses sound waves to create a detailed image of your eye to confirm the diagnosis of retinal detachment and identify any underlying causes.
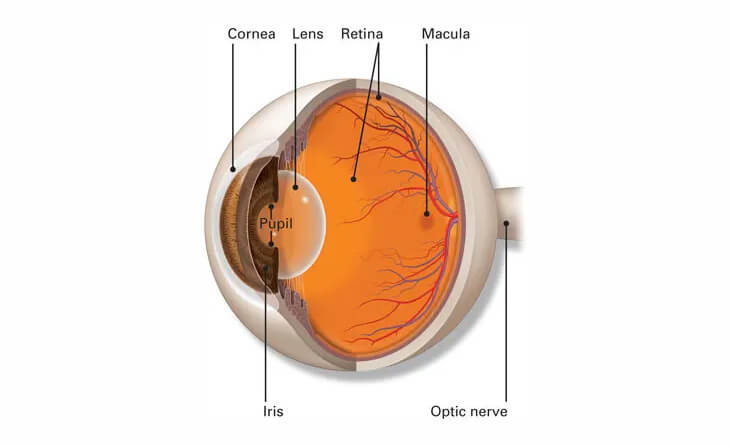
Prevention of Retinal Detachment
Unfortunately, there is no guaranteed way to prevent retinal detachment; however, there are a few steps that you can take to reduce your risk:
- Wear Protective Eyewear: If you participate in activities that could put your eyes at risk, such as sports or playing with tools, wear protective eyewear to help prevent eye injuries.
- Control Blood Sugar Levels: If you have diabetes or diabetic retinopathy, it is essential to control your blood sugar levels because high blood sugar can increase the risk of retinal detachment. If your doctor has advised you treatment for diabetic retinopathy like laser or intravitreal injcetions, get them done timely.
- Treat High Blood Pressure: High blood pressure can damage the blood vessels in the retina, increasing the risk of retinal detachment. If you have high blood pressure, take proper medication and adopt a healthy lifestyle, like exercising regularly, eating healthy food and avoiding smoking to control your blood pressure.
- Get Regular Eye Exams: Regular eye exams provide a comprehensive eye health assessment, enabling early detection and timely intervention for potential issues like retinal holes or tears, vascular occlusions and diabetic retinopathy.
- Monitor Symptoms: If you experience any of the symptoms of retinal detachment, such as floaters, sudden flashes, or a shadow or curtain-like effect moving across your visual field, see an eye specialist in Delhi immediately for diagnosis and treatment. These could be the signs of retinal detachment. Early detection can help you to prevent further vision loss.
Who is at Risk for Retinal Detachment?
Anyone can get retinal detachment; however, some people are more prone than others. These may include:
People Over the Age of 40: Retinal detachment is more common in older adults because the vitreous, the gel-like substance that fills the space between the lens and the retina, shrinks and pulls away from the retina with age. This can create tears or holes in the retina, leading to retinal detachment.
People With Myopia (Nearsightedness): People with nearsightedness are more likely to develop retinal detachment than people with normal vision because their eyes are longer and their retina is thinner and more stretched, which makes it more likely to tear.
People With Family History: If you have a family history of retinal detachment, you are at increased risk of developing the condition yourself because it can be inherited.
Trauma: Eye injuries during sports or due to other reasons can sometimes cause tears or holes in the retina, which can lead to detachment.
People with Certain Eye Conditions: Certain eye conditions, such as diabetic retinopathy and uveitis, can also increase your risk of retinal detachment.
Previous Eye Surgery: If you have had any eye surgery, like cataract surgery, in the past, you are at risk of retinal detachment.
People with history of retinal detachment in one eye : There is increased risk of retinal detachment in the other eye of a patient with retinal detachment in one eye.
If you are at increased risk of retinal detachment, get regular eye exams so your eye specialist in Delhi can monitor your condition for signs of retinal detachment.
Treatment of Retinal Detachment
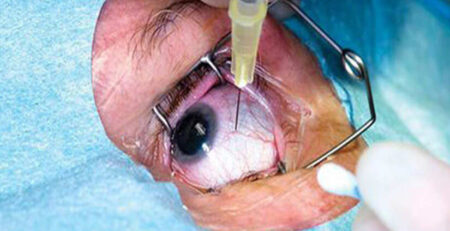
When the detachment is significant, the ultimate treatment for retinal detachment is surgery. Retinal detachment surgery aims to reattach the retina to the back of the eye. However, when there is a minor detachment or tear in the retina, your doctor may prescribe other procedures such as laser barrage (photocoagulation) and freezing (cryopexy).
Laser Barrage (Photocoagulation)
Laser barrage, or photocoagulation, addresses small retinal tears or holes that haven’t yet caused detachment.
Before the procedure, your eye specialist in Delhi will numb your eye with anesthetic eye drops to reduce the discomfort of the procedure. After, a specialized laser is used to create tiny burns on the retina, effectively sealing any leaks or tears and preventing further detachment.
The procedure is typically performed in an outpatient setting, which can take 10-30 minutes , depending on the extent of the tears/detachment.
Cryopexy
Cryopexy is another treatment option for retinal detachment that involves freezing the area around the retinal tear with a cold probe. This creates scar tissue that helps prevent the retinal detachment..
Surgery
If a larger area of the retina is detached, surgery is the only option to reattach it. Three common types of retinal detachment surgery are pneumatic retinopexy, scleral buckling, and vitrectomy.
1- Pneumatic Retinopexy
Pneumatic retinopexy is a minimally invasive surgery used to treat retinal detachments caused by small tears or holes in the retina, located in one area only.. During surgery, your doctor will inject a gas bubble into the vitreous cavity. The gas bubble pushes the retina back against the eye wall, and the tear or hole is sealed. The eye gradually absorbs the gas bubble over a few weeks. Once the gas bubble is in the right place, your eye specialist will use a laser or freezing treatment to seal the retinal tear or hole.
2- Scleral Buckling
Scleral buckling involves placing the silicone bands onto the sclera outside the white of the eye to support a detached retina and close the retinal break.
During the procedure, your doctor will create a small incision and strategically place the silicone band and buckle around the eye. The band is then carefully tightened to exert pressure on the sclera, causing the eye wall to push inward, thereby aiding in the reattachment of the detached retina.
The procedure is usually performed on a daycare basis. That means you can go home on the same day. Your eye specialist in Delhi may also use a freezing treatment or laser to seal retinal tears or holes.
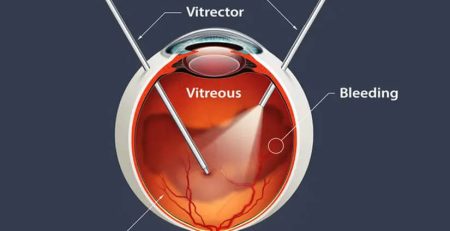
3- Vitrectomy
Vitrectomy is the primary treatment for tractional retinal detachments and complicated rhegmatogenous retinal detachments with multiple breaks, no breaks and fibrosis. During vitrectomy, the vitreous gel, a clear substance that fills the centre of the eye, is removed from the eye. This gel is replaced with a gas or silicone oil bubble that work as tamponade to reattach the retina. After the surgery, you may need to maintain a specific head position for several days to allow the gas bubble/silicon oil to push the retina back into place and promote healing effectively.
4- Combined approach
Sometimes, your eye surgeon may prefer a combined approach of scleral buckling and vitreactomy. This is also preferred in severe advance cases of retinal detachment.
The type of surgery that is right for you will depend on the type, severity and location of your retinal detachment. For exudative retinal detachment, it is essential to treat the underlying causes of fluid accumulation. Treating the underlying causes can help to reattach the retina to its normal position.
Vision/Recovery After Retinal Detachment Surgery
Each person’s body is unique; therefore, they respond differently to retinal detachment surgery. Some people may resume their regular activities within a few weeks, while others may require several months to recover properly.
Typically, it takes at least three months to ensure that the retina has been properly reattached and for effective vision recovery.
Here is a general outline of what you can expect after retinal detachment surgery:
Immediately After Surgery: After retinal detachment surgery, the treated eye is shielded with protective covers or patches. After the surgery, you can experience some discomfort and blurred vision, which gets better in 2-4 days.
First 2 Weeks: In the first two weeks, you can experience mild discomfort, floaters, flashes of light, blurry vision, swelling, and redness in the treated eye. Your eye specialist in Delhi will provide medication to manage pain and, potentially, eye drops to reduce inflammation and prevent infection.
During this time, you need to rest properly and limit your activity level. Avoid strenuous activities and driving.
If a gas bubble or silicon oil is injected into your eye, you will need to maintain a particular position, face-down/ sideways/ upright position, at all times.
Your eye specialist in Delhi will determine the duration of this positioning, which may range from a few days to a week or more. Adhering to these instructions helps in keeping the retina attached and prevents further eye complications.
Week 3 and 4: After 3 weeks, any discomfort, swelling, or redness should gradually subside. While floaters and flashing lights may persist, they will eventually fade away. You can resume your normal activities after getting the clearance from your doctor.
If a gas bubble is injected into your eye, you should avoid altitude changes, such as air travel, mountain climbing, and scuba diving, for up to 6-8 weeks, even if your doctor has approved physical activity. These precautions help prevent the bubble from expanding and causing increased eye pressure.
Within 4 to 6 weeks following the procedure, you should begin to notice improvements in your vision. However, it may take several months for your vision to stabilize fully. The complete healing of your retina may take a year.

Precautions After Retinal Detachment Surgery
Like any surgical procedure, taking some precautions is important to help your eye heal properly and prevent further complications after retinal detachment surgery. Here are some tips that you can follow to boost your healing process:
Rest and Limit Activity: During the first few weeks after retinal detachment surgery, it’s essential to rest and avoid strenuous activities such as exercise, heavy lifting, and strenuous work. Excessive activity can put a strain on the healing eye and increase the risk of infection and other complications.
Maintain Proper Head Positioning: If a gas bubble or silicon oil is injected into your eye, you may need to maintain a particular head position for a specified period. This helps keep the bubble in place and promotes healing. Your doctor will instruct you on the duration and proper technique for positioning.
Do Not Rub Your Eyes: Keep your hands clean and avoid touching or rubbing the treated eye. This can increase the risk of infection and disrupt the healing process.
Use Prescribed Eye Drops: Your eye specialist in Delhi may prescribe eye drops to help reduce inflammation and prevent infection. Be sure to use the eye drops as directed and to wash your hands before and after using them.
Avoid Altitude Changes: If a gas bubble is injected into your eye, avoid altitude changes for up to 6-8 weeks. This may include avoiding air travel, mountain climbing, and scuba diving. Altitude changes can cause the bubble to expand and increase eye pressure, leading to complications.
Limit Driving: Avoid driving until your doctor instructs you to do so. During the recovery phase, you may have vision disturbances and impaired coordination, which can make driving unsafe.
Maintain a Healthy Lifestyle: Adopt a healthy lifestyle by eating a balanced diet, getting enough sleep, and managing stress. These factors contribute to overall well-being and support the healing process after retinal detachment surgery.
Attend Follow-up Appointments: After the surgery, your doctor may schedule follow-up appointments to monitor your healing progress, address any concerns, and adjust your treatment plan if needed. You should attend all these appointments with your doctor.
Seek Immediate Medical Attention for Concerns: If you experience any sudden changes in vision, increased pain, severe redness, or unusual discharge from the eye, contact your doctor immediately. These could be signs of complications that require prompt attention.
Cost of Retinal Detachment Surgery
Retinal detachment surgery is a complex procedure that involves reattaching the retina to its normal position. Different techniques are used depending on the severity of the condition; therefore, the price varies for each procedure—for example, scleral buckling costs between Rs. 25000 and Rs. 35000 while vitrectomy costs between Rs. 35000 and Rs. 65000. On the other hand, combining buckling and vitrectomy can cost between Rs. 55000 to Rs. 65000.
However, this cost for retinal detachment surgery varies from patient to patient, depending on several factors. These factors may include:
The Severity of the Condition: The severity of retinal detachment can significantly increase the cost of surgery because the severe retinal detachment may require additional procedures, more extended hospital stays, and more post-operative care, which can increase the overall cost.
Type of Method Chosen for Treatment: There are three main types of retinal detachment surgeries: pneumatic retinopexy, scleral buckling, and vitrectomy. Pneumatic retinopexy and scleral buckling are less invasive procedures for treating small retinal tears and are less expensive. On the other hand, vitrectomy is generally more costly, as it is a more complex procedure that requires more specialized equipment and expertise.
Surgeon’s Experience: An experienced, certified, skilled eye specialist in Delhi will likely charge more because they can handle complex cases and achieve successful outcomes. However, it is crucial to choose an experienced and qualified retinal specialist, even if their fees are higher. After all, your vision is at stake.
Location of the Clinic: The cost of retinal detachment surgery can also vary depending on the clinic’s location. Surgery performed in urban areas may be more expensive than in rural areas because the cost of living in urban areas is higher than in rural areas.
Additional Costs: In addition to the cost of the surgery itself, there are several other costs that patients may need to consider, such as the cost of anesthesia, the cost of medications, and the cost of follow-up appointments.
What if My Retinal Detachment Surgery is Not Successful?
Fortunately, the success rate of retinal detachment surgery is very high, with over 90% of people experiencing successful retina reattachment. Although rare, there are chances that your retinal detachment surgery can be unsuccessful.
If retinal detachment surgery is not successful, the retina may detach again. This can lead to further vision loss or even blindness. The risk of re-detachment is highest in the first few months after surgery, but it can happen at any time. In rare cases, retinal detachment surgery can lead to other complications, such as cataracts, glaucoma, or infection.
Several reasons can affect the success rate of retinal detachment surgery. These include:
- The severity of the retinal detachment and the extent of retinal tearing.
- Previous retinal detachment surgery.
- Certain medical conditions, such as diabetes and high blood pressure.
- Proliferative vitreoretinopathy (PVR): This is a condition in which scar tissue forms on the retina, making it difficult to reattach.
If your retinal detachment surgery is unsuccessful, your eye specialist in Delhi may recommend additional surgery or other treatments. The goal of treatment is to reattach the retina and prevent further vision loss.
Conclusion!
Retinal detachment is a serious eye condition that can lead to vision loss if left untreated. If you experience retinal detachment symptoms, it is important to see an eye doctor immediately. With early diagnosis and treatment like retinal detachment surgery, most people with retinal detachment can have their vision restored or preserved.
If you are looking for an effective treatment for retinal detachment, schedule your consultation with Dr Anisha Gupta, an experienced eye specialist in Delhi. She will assess your eye condition and prescribe a suitable treatment plan.