What is the Most Common Cause of Retinal Detachment?
Retinal detachment is a serious eye condition that occurs when the retina, the light-sensitive tissue at the back of the eye, is pulled away from its normal position. Retinal detachment causes a separation between the retinal cells and the layer of blood vessels responsible for supplying oxygen and nutrients to the eye. If left untreated for an extended period, the chances of experiencing permanent vision loss in the affected eye significantly increase. There are several causes of retinal detachment, and understanding these causes can help to find an effective retinal detachment treatment.
In this blog, we will discuss the most common causes of retinal detachment. Keep reading!
Causes of Retinal Detachment
Consulting the eye specialist in Delhi can help you to determine the causes of retinal detachment. Rhegmatogenous retinal detachment is the most common type of retinal detachment, and retinal tear is the most common cause of rhegmatogenous retinal detachment. Other reasons for retinal detachment based on the types are as follows:
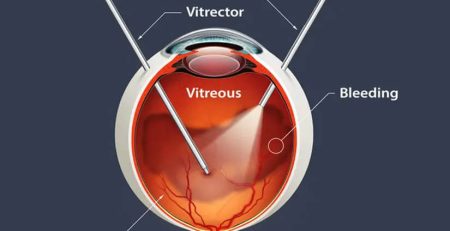
Rhegmatogenous Retinal Detachment: Rhegmatogenous retinal detachment is the most common form of retinal detachment and is often related to ageing. This condition occurs when a tear or hole develops in the retina, allowing the gel-like substance called the vitreous humour to leak behind the retina. The most common causes of retinal tear leading to rhegmatogenous retinal detachment include:
- Ageing causes changes in vitreous (gel inside the eye)
- High myopia (nearsightedness)
- Post-surgery
- Post-trauma
- Retinal Lattices and holes
Tractional Retinal Detachment: Tractional retinal detachment is less common than rhegmatogenous retinal detachment, where the scar tissues on the retinal surface pull the retina from its position. The most prevalent cause of tractional retinal detachment is diabetes because high blood sugar damages the blood vessels in the retina, leading to abnormal growth of scar tissue. These scar tissues pull the retina and cause vision problems. Other causes may include:
- Blood pressure
- Other inflammatory eye diseases like vasculitis and uveitis

Exudative Retinal Detachment: Exudative retinal detachment differs from the other two types, as it typically results from fluid buildup beneath the retina. It does not result from any break or tear in the retina. When an excessive amount of fluid becomes trapped behind your retina, it can potentially displace the retina away from the rear of your eye, resulting in its detachment. The causes of exudative retinal detachment are:
- Swelling inside the eye : Uveitis or scleritis
- Eye Tumors
- Central serous chorioretinopathy
- Age-related macular degeneration (AMD)
Early symptoms of Retinal detachment are:
- Sudden onset of floaters
- Flashes of light
- Blurred or distorted vision
- A shadow or curtain descending over your field of vision
If you experience any of these symptoms, consult an eye specialist immediately for appropriate retinal detachment treatment. Early diagnosis and treatment are essential to prevent further detachment and preserve your vision.
Treatment option for Retinal Detachment
Retinal detachment surgery is the most effective treatment to repair the detached retina. The specific procedure used depends on the type and severity of the detachment. Some common surgical approaches include:
- Laser therapy or cryopexy : This is done if the retinal detachment has not started or is in very early stage
- Pneumatic (gas bubble) retinopexy : Done in early stages in specific cases
- Scleral buckle.
Conclusion!
Retinal detachment is a serious eye condition that can lead to permanent vision loss if left untreated. Understanding the common causes, risk factors, and symptoms is essential for early detection and timely intervention. Regular eye exams and control over underlying medical conditions, such as diabetes and hypertension, can significantly reduce the risk of retinal detachment.
If you ever experience any symptoms related to retinal detachment, schedule your consultation with Dr. Anisha Gupta for retinal detachment treatment.